Slipped disc can be an extremely painful condition. Find out how it’s caused, what the risk factors are, and how to diagnose, prevent, and treat the condition.
What is a slipped disc?
A slipped disc (also called herniated or prolapsed disc) is when the intervertebral disc (the disc between your vertebral bones) bulges or protrudes out.
Normally, the intervertebral disc is present between the bones present in our spine (these bones are called vertebrae). They serve as a cushion between the bones, permit movement between them, and act as shock absorbers. When this disc starts protruding out, it leads to back pain and discomfort.
How is a slipped disc caused?
Most commonly, it occurs due to age-related changes as the disc becomes stiff and more prone to damage with increasing age. Rarely, it may also occur as a result of trauma, falling, or lifting heavy objects.
What are the risk factors for developing slipped disc?
It most commonly affects men between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Factors that put you at increased risk include:
- Excessive body weight or obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- A physically demanding or laborious job requiring a lot of exertion and heavy lifting
- Smoking
- Positive family history
What are the symptoms of slipped disc?
Symptoms include :
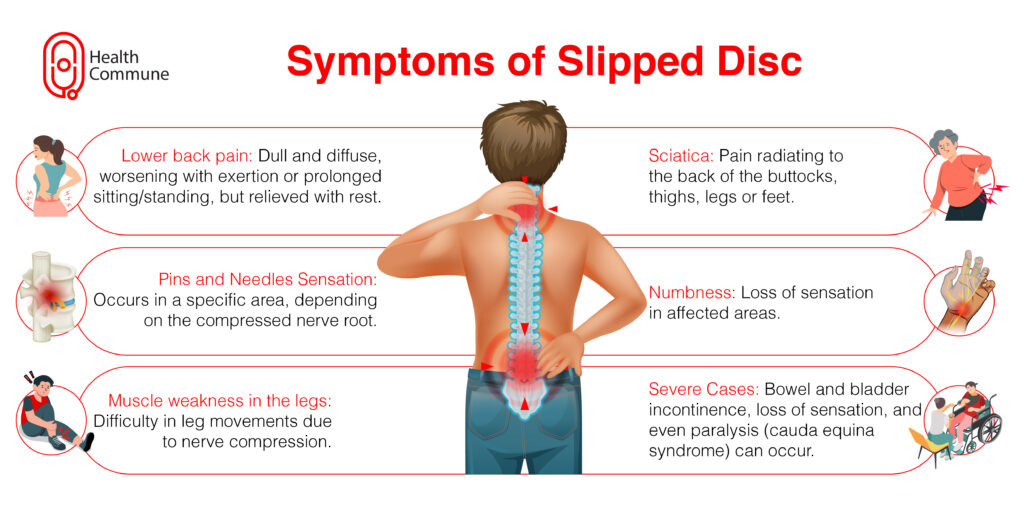
- Lower back pain: Normally, the pain is dull and diffuse and develops over a period of time. It gets worse on exertion or standing or sitting for long durations and is relieved on taking rest. In case your sciatica is offset by some kind of trauma or injury, it can develop suddenly and is severe in such cases. The muscles get spasmed and cause great difficulty in movement
- Pain radiating to the back of the buttocks, thighs, legs, or feet (sciatica): Sometimes this pain can start when you walk and subside after taking rest
- Pins and needles sensation in a particular area (depending on the nerve root that gets compressed)
- Numbness
- Muscle weakness in the legs
- In severe cases, there can be bowel and bladder incontinence, loss of sensation, and even paralysis (cauda equina syndrome)
How slipped disc diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about symptoms in detail and carry out a thorough physical examination. This includes:
- Checking your posture and if you’re able to move normally
- Checking for tenderness and localising the source of your pain
- Asking you to lie down and lifting your leg in various positions to check if your nerve is compressed
- Neurological examination: In cases of muscle weakness, numbness or tingling sensation, bowel and bladder dysfunction.Your doctor will carry out an in-depth neurological examination to reveal the underlying problem
They can ask you to undergo the following tests:
- Plain X-ray, which cannot confirm the diagnosis but is helpful in ruling out any bone diseases
- CT scan
- MRI scan, the gold standard of diagnosis
- Electromyography (EMG), which is rarely required but is helpful in cases of multiple slipped discs
How is slipped disc treated?
Most cases require only conservation treatment. This includes:
- Your doctor may ask you to rest on a hard bed for 2-4 days because it is the most important treatment
- Avoid straining and lifting heavy objects
- Keeping an ice pack on the affected area
- Mild painkillers such as paracetamol, ibuprofen, or other NSAIDs
- Muscle relaxants to help relieve your muscle spasm
- Physiotherapy to help reduce your pain and strengthen your back muscles
- Steroid injections, which are directly injected into your spine
When is surgery recommended for a slipped disc?
Surgery is usually recommended when:
- Conservative treatment fails to improve your symptoms, even after 4-6 weeks
- You develop pain, weakness in your legs, and bowel or bladder dysfunction due to severe nerve compression (also called cauda equina syndrome)
What are the surgeries done for slipped disc?
Surgical interventions include:
- Discectomy is a surgical procedure in which the protruding or herniated part of an intervertebral disc in the spine is removed.
- Laminotomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing a small portion of the lamina, to create more space and relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
- Laminectomy, where part of the bones on both sides of the vertebrae are removed to make more room for the intervertebral disc
- Hemi-laminectomy, where part of the bones on both sides of the vertebrae are removed to make more room for the intervertebral disc
Can a slipped disc heal on its own?
Yes, mild cases can usually go away on their own or can be managed with conservative treatment.
How long does it take for a slipped disc to heal?
Mild cases usually take about 4-6 weeks to heal.
How can I prevent a slipped disc?
Preventative measures include:
- Improving your posture to prevent back pain and degenerative changes that come with age
- Leading an active lifestyle with regular exercise to strengthen your back muscles
- Losing weight to reduce stress on your spine
- Quitting smoking





