Did you know that 197.3 million people in India suffer from mental disorders, of which 45.7 million suffer from depression? Each person experiences depression in different ways, which is difficult to find out. This article explains depression, its causes, symptoms, and management.
What is depression?
Depression is a mood disorder that signifies sadness that is severe and persistent and interferes with normal functioning. This usually affects both the mind and body by affecting the sleep, appetite, and energy levels of the person.
What are the types of depression?
According to the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), depressive disorders are classified into
- Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder
- Major depressive disorder
- Persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)
- Premenstrual dysphoric disorder
- Depressive disorder due to another medical condition
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder
A condition in which children or adolescents experience continued irritability, anger, and frequent temper outbursts that are severe and beyond expectations.
Major depressive disorder
When an individual persistently has a low mood, a lack of interest in pleasurable activities, a feeling of guilt and worthlessness, poor concentration, and suicidal thoughts. are considered to have major depression.
Persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)
When the depressive symptoms last for many years and interfere with your relationships, work, and daily activities.
Depressive disorder due to another medical condition
Certain diseases like stroke, hypothyroidism, Parkinson’s disease, and traumatic brain. The injury also causes a persistent or predominant depressed mood.
What are the causes of depression?
The leading causes include
- Changes in brain chemistry: chemical imbalance in parts of the brain that control mood, sleep, and thoughts
- Early childhood trauma
- Family history
- Medical conditions like stroke, cancer, heart attack, and Parkinson’s disease
- Substance abuse with alcohol and narcotics
- Emotional pain or chronic pain associated with the disease that lasts for a longer duration
- Post-partum, menstrual, or menopause fluctuations in estrogen or progesterone hormones.
What are the risk factors of depression?
- Being a women increase the chances of depression
- Genetic factors and family history
- Socioeconomic status, like financial problems and low social status
- Use of certain medications, such as birth control pills, corticosteroids, and beta blockers
- Lack of vitamin D
- Substance abuse
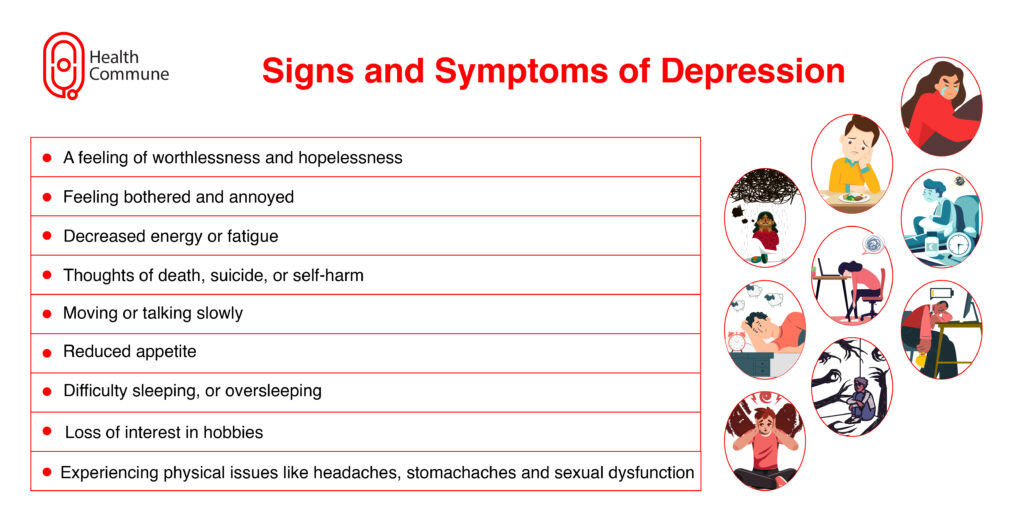
What are the signs and symptoms of depression?
General signs and symptoms
- A feeling of worthlessness and hopelessness
- Feeling bothered and annoyed
- Decreased energy or fatigue
- Thoughts of death, suicide, or self-harm
- Moving or talking slowly
- Reduced appetite
- Difficulty sleeping, or oversleeping
- Loss of interest in hobbies
- Experiencing physical issues like headaches, stomachaches and sexual dysfunction
How is depression diagnosed?
There are no diagnostic tests available for depression. It is diagnosed mainly based on physical findings and medical history. However, certain lab tests may be useful to exclude a medical illness that may present as a major depressive disorder. This includes the following:
- Complete blood count
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test
- Electrolytes like calcium, phosphate, and magnesium
- Blood alcohol level
- Vitamin B12
- Liver function
- Blood urea, nitrogen, and creatinine tests
How is depression treated?
Almost 80-90% of people who seek treatment for depression respond to the treatment effectively. Treatment options include:
Psychotherapy involves talking with the therapist, who identifies and changes your unhealthy thoughts and emotions. Types include:
- Cognitive behavioural therapy is when the therapist identifies unhealthy thoughts and checks how they may be causing harmful behaviours and reactions about yourself.
- Dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT) is similar to CBT but emphasises more on validation, or accepting uncomfortable thoughts, feelings, and behaviours, rather than fighting them.
- Psychodynamic therapy helps you cope with your daily activities.
Medications can help change the brain chemistry that causes depression. This includes:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) treat depression by increasing the availability of the neurotransmitter (chemical messengers that carry messages from one neuron to the other) serotonin in the brain.
E.g., citalopram and escitalopram - Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) work by increasing the amount of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain.
E.g., duloxetine and desvenlafaxine - Tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants are similar to SNRIs in that they increase the amount of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain but have more side effects compared to SNRIs.
E.g., amitriptyline and doxepin - Monoamine oxidase inhibitors work by increasing the level of neurotransmitters like norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine, and tyramine in your brain.
E.g., isocarboxazid and phenelzine - N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists work by increasing levels of the neurotransmitter glutamate in the brain.
E.g., esketamine
Light therapy, which includes exposure to white light, helps to improve your mood and reduce symptoms of depression.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) uses electrical currents to induce seizures, which reduces the symptoms of clinical depression.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation is done using a coil that can be placed against your scalp, which will send brief magnetic impulses to stimulate the nerve cells in your brain.
Alternative therapies like meditation, acupuncture, and massage are found to be effective in reducing the symptoms of depression.
How can depression be prevented?
You cannot prevent depression, but the risk can be reduced by:
- Practising activities like exercise, yoga, and meditation
- Managing stress with coping strategies
- Maintaining a proper sleep routine





