Osteoarthritis is a widespread condition of the joints. It is most commonly found in adults aged 45 and above, but sometimes younger adults may also develop it. It can affect any joints in our body, but the most common areas are joints that bear weight, like the knees and the hips. Let us now understand the causes, symptoms, risks, treatment, and ways to prevent it.
What is osteoarthritis?
What are the types of osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is mainly of two types:
Primary osteoarthritis:
- The most common type of osteoarthritis
- Seen in older populations due to age-related degenerative change
- It occurs in any joint like the knee, hip, spine, fingers, great toe, etc.
Secondary osteoarthritis: This occurs when there is a pre-existing joint deformity like:
- Injury
- Sports-related trauma
- Inflammatory arthritis, like rheumatoid arthritis
- Certain genetic disorders, like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (a condition that affects the connective tissue that supports organs and other tissues throughout the body)
What are the risk factors for osteoarthritis?
Wear and tear on your joints causes osteoarthritis, and the following factors contribute to the condition:
- Age: People over 40 years of age are more vulnerable to developing osteoarthritis
- Gender: Women are more affected than men
- Obesity: This increases the risk to weight-bearing joints such as the knees and the hip
- Joint injury: An operation or a major injury might put you at risk of osteoarthritis
Joint abnormalities - Genetic factors: Rare forms of osteoarthritis may be linked to mutations in the genes that affect collagen protein
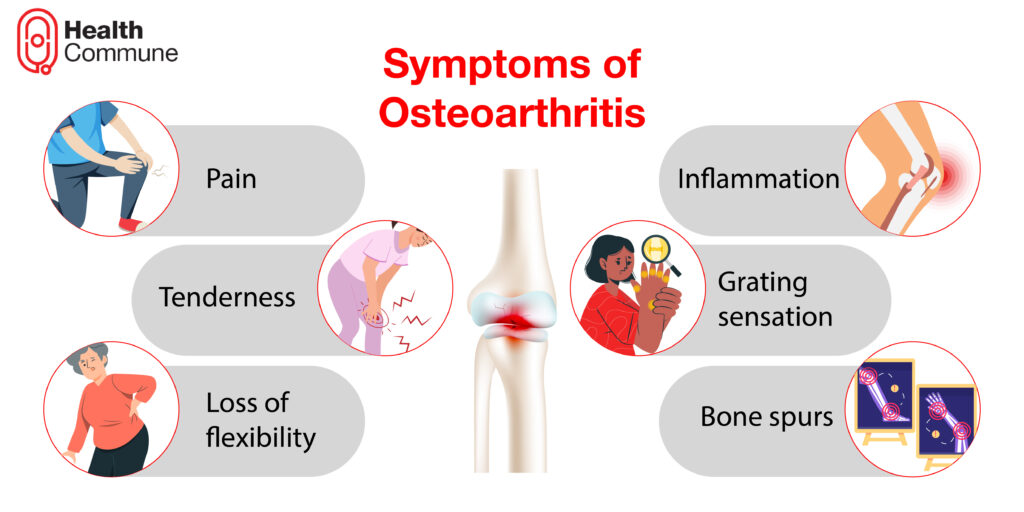
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis?
- Pain during or after movement of the joints
- Inflammation in the tissues surrounding the joints
- Tenderness
- Grating sensation: A crackling sound may be heard while you make the joints move
- Loss of flexibility
- Bone spurs (extra bits of bone) may develop around the affected joint
How is osteoarthritis diagnosed?
The diagnosis of osteoarthritis is usually based on your symptoms, your medical history, and any physical signs that the doctor finds while examining your joints.
- While taking medical history, your doctor asks you about your symptoms, how these symptoms affect your day-to-day practices, and if you have any other medical conditions
- During the physical examination, doctors examine your joints for swelling, tenderness over the joints, bony swelling, restricted movement, joint instability, and creaking or grating sounds of the joint
- Imaging tests like X-rays and, in case they suspect some other underlying pathology, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- In some instances, a joint fluid analysis (fluid drawn from the affected joint using a needle) might be done to determine whether the pain is caused by gout or some other infections
What are the treatments for osteoarthritis?
Although there is no cure for osteoarthritis, there are treatments that can provide relief from the symptoms and help you manage your daily activities. These include:
Medications
- Pain relief medications: Drugs like paracetamol help reduce mild to moderate pain
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and diclofenac are easily available in over-the-counter pharmacies and are effective for some joints, like hands and knees
- Creams, gels, and ointments: These are applied to the concerned joint to relieve osteoarthritis pain
- Steroid injections: injections of long-acting steroids are given directly into a particularly painful joint. This helps improve pain for several weeks or months, especially in the knee and thumb
- Hyaluronic acid injections: Hyaluronan is a natural lubricant in your joints. These injections are sometimes used as a treatment of choice for osteoarthritis
Therapy
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist demonstrates exercises that help you strengthen the muscles around your joints, increase your flexibility, and relieve pain
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS): In this procedure, a low-voltage electrical current is used to relieve pain. Some people with knee and hip osteoarthritis benefit from it in the short term
- Occupational therapy: An occupational therapist can assist you in finding ways to perform daily tasks without putting additional strain on your joint
Surgery
- Knee osteotomy: A knee osteotomy is done when one side of your knee is damaged more than the other. The damaged areas are removed surgically
- Replacement of a joint: Your surgeon will remove your damaged joint surfaces and replace them with plastic and metal parts during joint replacement surgery
What are the tips for managing my osteoarthritis pain?
The pain caused by osteoarthritis is very intense and can affect your day-to-day activities. Here are some tips to manage your pain:
- Applying heat and cold packs can relieve pain and swelling
- Splints and other supports, like braces, are available for patients affected by the alignment of joints. It’s not recommended to wear splints or supports at all times, as this may lead to the weakening of muscles
- Choosing comfortable footwear is very essential, as this helps to relieve pain. In general, an ideal shoe would have a thick but soft sole, soft uppers, and plenty of room at the toes and at the ball of the feet
- Walking aids like walking sticks prevent you from falling at certain times
- Maintaining a good posture that puts less strain on your joints makes you feel more relaxed
What lifestyle changes should I make?
Certain lifestyle changes help you cope with the disease. These are:
- Low-impact exercise can improve your endurance while also strengthening the muscles surrounding your joint, making it more stable. Examples include walking and bicycling
- Extra weight puts additional strain on your weight-bearing joints, such as your knees and hips. Even minor weight loss can relieve stress and pain.
- Tai chi and yoga may lessen the pain associated with osteoarthritis and increase mobility; many individuals utilise these therapies to alleviate stress in their life. They are coupled with deep breathing and soft movements.





