What is In-vitro fertilisation (IVF)?
In-vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a type of assisted reproductive technology. In this, your egg is combined with the sperm in a petri dish to achieve fertilisation outside your womb and then implanted in the uterus. It is a breakthrough technology that continues to help many couples with infertility issues have healthy babies.
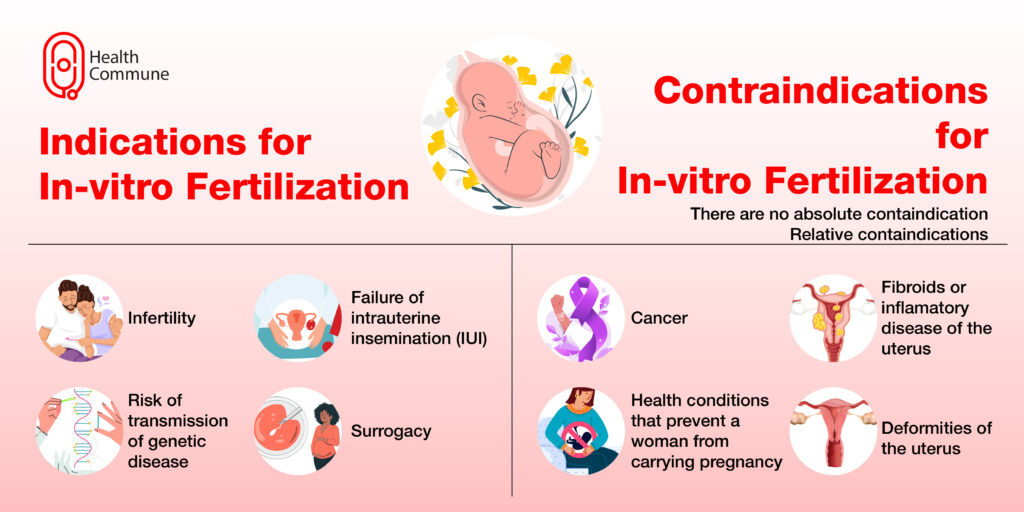
What are the indications of IVF?
- Unexplained infertility
- To prevent the transmission of genetic diseases , the embryo is tested for genetic problems before implantation
- In instances where intrauterine insemination (IUI) fails
- Infertility issues in women :
- Issues in the fallopian tubes
- Endometriosis
- Premature ovarian Insufficiency (a condition in which a woman’s ovaries stop functioning normally even though she has not yet attained menopause)
- Decreased ovarian reserve
- Fibroids in the uterus
- In women who have undergone tubal ligation (the procedure of cutting or blocking fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy), IVF is an alternative to reversal surgery
- For women who wish to preserve their fertility (treatment for health conditions like cancer can affect your ability to get pregnant. In such conditions, the egg or embryo can be frozen, preserved in the lab, and used later through IVF)
- When a surrogate (gestational carrier) is employed, when a woman doesn’t have a functional uterus or health conditions prevent them from being pregnant, another person can carry the pregnancy
- Infertility issues in men :
- Poor quality semen
- Decreased sperm count, sperm motility or altered shape and size of the sperm
Are there any contraindications for IVF?
While there are no absolute contraindications, certain conditions, like fibroids in the uterus or inflammatory diseases, should be treated before IVF is attempted. If any health condition prevents a woman from carrying the pregnancy, such as cancer, deformities of the uterus, etc., then IVF can be tried with the help of a gestational carrier (surrogate).
What are the preparations for IVF?
Before your IVF cycle starts:
- You will be required to sign a consent form that informs you about the procedure, its risks and complications
- The following screening tests are done beforehand :
- Analysis of semen
- Analysis of the quantity and quality of your eggs by testing the concentration of certain hormones (follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), oestrogen, and anti-mullerian hormone) in your blood
- Screening for any infectious diseases like HIV
- Baseline ultrasound
- Examination of the uterus – through sonohysterography (which uses sound waves to look inside the uterus and see the lining) and hysteroscopy (a slender telescope is inserted through the vagina into the cervix and to the uterus)
- Downregulation hormone injections are started as directed by your fertility specialist. This is done to control the release and maturation of the eggs during the treatment period
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) injections: When down-regulation is confirmed by your blood tests and ultrasound, FSH injections are started. The dose of the drug depends on your previous baseline hormone results and your response to previous stimulated cycles
- After your baseline scan, the dosage of your FSH is confirmed
- Hormone blood tests: Your blood sample will be taken for hormone assessment and scanning to check the response
These results will be used to adjust your FSH injections, and then the date and time for your final hCG injection will be decided. The hCG injection will mature and release your eggs within the follicles. Approximately after 36 hours, your eggs will be retrieved.
What happens during the IVF procedure?
The IVF procedure is done step-by-step:
1. Stimulation
Multiple eggs are required for the IVF procedure as not all eggs will get fertilised, while others may not develop properly after fertilisation. Normally, your body produces only one egg per month. You will be given hormones and medicines to induce the production and maturation of multiple eggs, prevent their premature release and prepare your uterus lining for receiving the fertilised embryo. Your doctor will monitor the process through transvaginal ultrasounds and blood tests.
2. Egg retrieval
Just before ovulation, your egg retrieval process takes place through a 20-30 minutes surgical procedure called follicular aspiration. During this step, you will be given anaesthesia to relieve your pain.
Your egg is retrieved aseptically through the vaginal route under ultrasound guidance. A thin needle is connected to a suction device that goes into your vagina, into your ovary, and then the egg-containing follicle. The needle will suction your eggs and fluid out of each follicle. During egg retrieval, you may experience cramping or a feeling of pressure.
3. Insemination and fertilisation
In IVF, the semen sample is collected from your partner. The sperm are then incubated, and during this, a sperm enters your egg.
If your doctor feels that fertilisation chances are low, he will decide to go for an intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). In ICSI, your doctor will directly inject healthy sperm into your mature egg. For a successful IVF, sperm density and sperm motility are two important criteria required.
4. Embryo culture
Your doctor will be monitoring the fertilised eggs kept in the incubator to ensure they’re dividing and developing well. To keep up with the nutritional requirements of the growing embryos, the culture medium is changed at regular intervals.
These embryos undergo cleavage into a complex structure, and on the 3rd or 4th day, enter a stage called the morula. the Morula enters the last stage of embryonic development on the 5th day. It is referred to as a blastocyst at this stage. A blastocyst transfer increases your chances of conception.
While the embryo is growing in the incubator, a small sample is removed and tested for genetic diseases. This test is known as a preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) identifies abnormal embryos so that the unaffected embryos can be selected for the transfer. This test can give you a healthy baby and reduce the risk of genetic disorders in the future.
5. Embryo transfer
Embryo transfer will take place when the embryo has developed enough to be implanted. It will take approximately 3-5 days after egg retrieval and fertilisation for its development.
A thin tube (catheter) that contains your embryo is inserted inside your vagina, through your cervix, and up into your womb. When the embryo gets implanted into your uterine wall and starts growing, a simple blood test will determine your pregnancy after 10-12 days.
How many embryos will be transferred and what happens to the untransferred embryos?
The Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) recommends the transfer of 2-3 embryos depending on their stage of development. The transfer of multiple embryos may result in multiple pregnancies which can be risky for both the mother and the babies.
The unused embryos are frozen, donated or discarded based on the preferences of the couple.
How long does it take to get results with IVF?
After embryo transfer, you can resume your daily activities. You may be advised to avoid strenuous physical activities during this period.
About 2 weeks after egg retrieval, your doctor will perform a blood test to determine if you are pregnant.
- If you are pregnant, you will be referred for further management to an obstetrician
- If you are not pregnant, you will be asked to stop progesterone hormone supplements, and you will get your period within a week. If you experience unusual bleeding or do not get your period, contact your doctor
What if IVF fails?
Are IVF-born babies healthy?
Are there any risks to IVF?
- Multiple pregnancies : since more than one embryo is transferred, it can result in having twins, triplets or more
- Miscarriage
- Ectopic pregnancy : implantation of the fertilised egg outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube
- Birth defects in the babies
- Complications due to the egg retrieval procedure
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome : Due to the injection of fertility hormones, the ovaries can become painful and swollen, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhoea, and vomiting, which may last for weeks together





