What is a CT scan?
Why is a CT scan advised?
- To diagnose internal bleeding, injuries, cancer
- To determine the exact site of a tumour, infection, or blood clot
- To guide procedures such as biopsy, surgery and radiation therapy
- To evaluate the efficiency and outcome of treatment
What is a contrast CT scan?
Is a CT scan harmful to me?
What are the risks of a CT scan?
- Exposure to radiation
The dose of X-ray radiation used in CT is higher than that used in conventional X-rays. This may slightly increase your risk of cancer. But the information provided is vital for the diagnosis of your condition and for planning its treatment. The benefits of CT scans outweigh the potential risks. Talk to your doctor if you are concerned about the risk of cancer.
- Allergy to contrast media
The contrast media that you drink or are injected with are usually safe. However, some people may develop allergic reactions. If you have a previous history of allergies to iodine or contrast agents, let your doctor know about it beforehand. Even if there is an allergy, it will usually be mild in the form of itching or rashes. In case there is a severe allergic reaction, your radiology centre will be equipped to handle it
- Risk in pregnant women
The X-ray radiation used in CT scans has not been shown to cause any damage to the foetus. However, there may be a slight risk of the baby developing cancer as a child if exposed to radiation. Inform your doctors beforehand if you suspect that you are pregnant.
What is the usual duration of a CT scan?
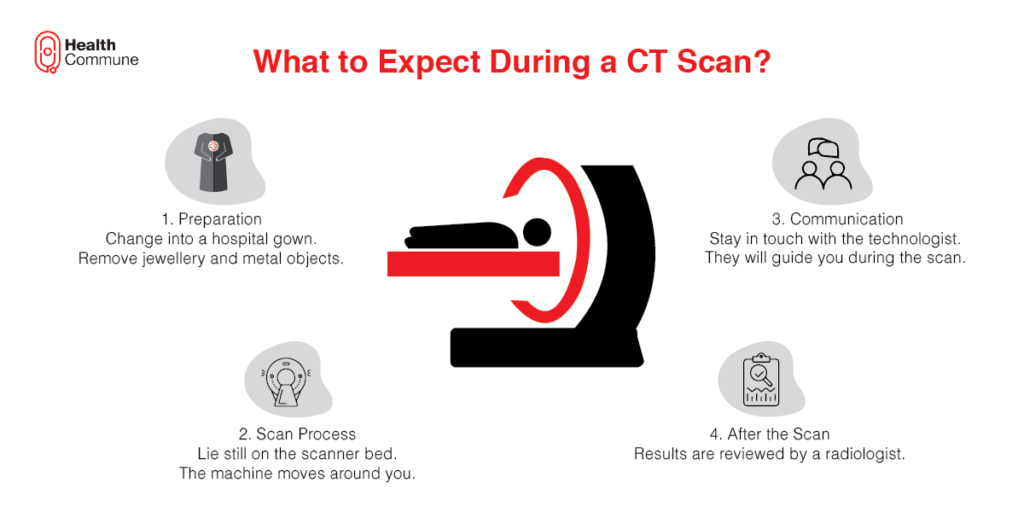
What do I expect during the scan?
How do I overcome my claustrophobia during a CT scan?
How do I prepare for a CT scan?
- Remove all the jewellery and any removable metallic objects that you’re wearing
- Take off your clothes and switch to the hospital gown provided by the radiology centre
- Avoid eating and drinking at least 4 hours before the scan if you are going to have an oral contrast CT study